Search
Categories
More
Tags
Definition of induction forging
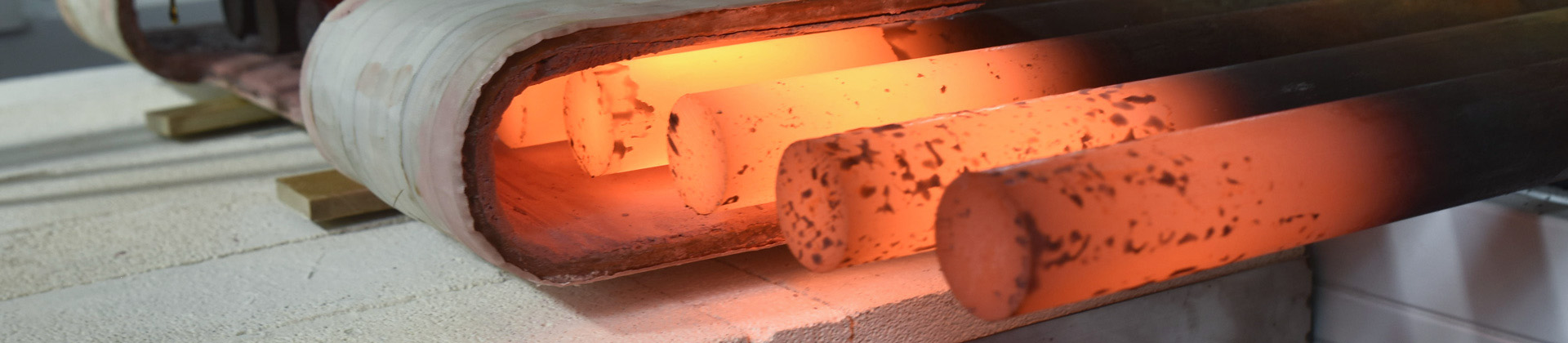
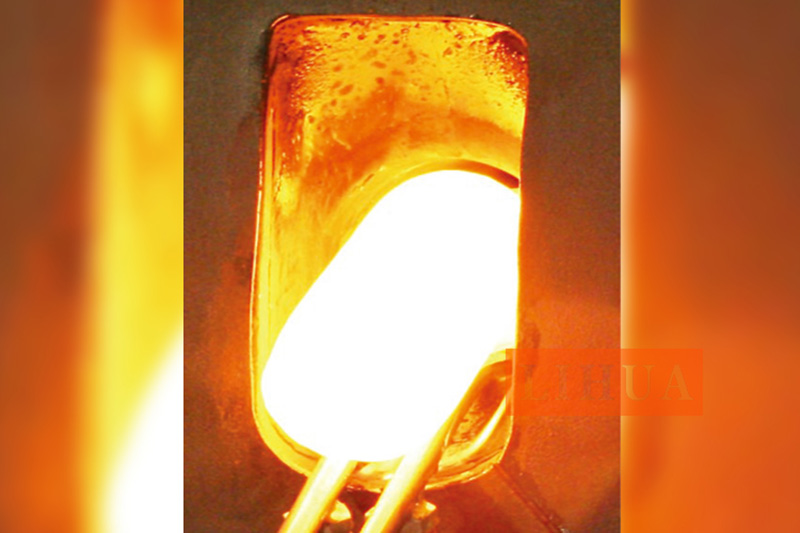
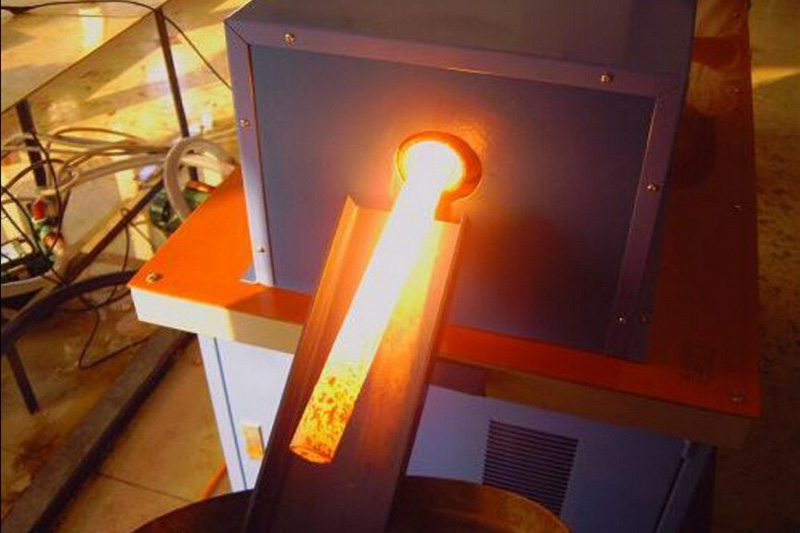
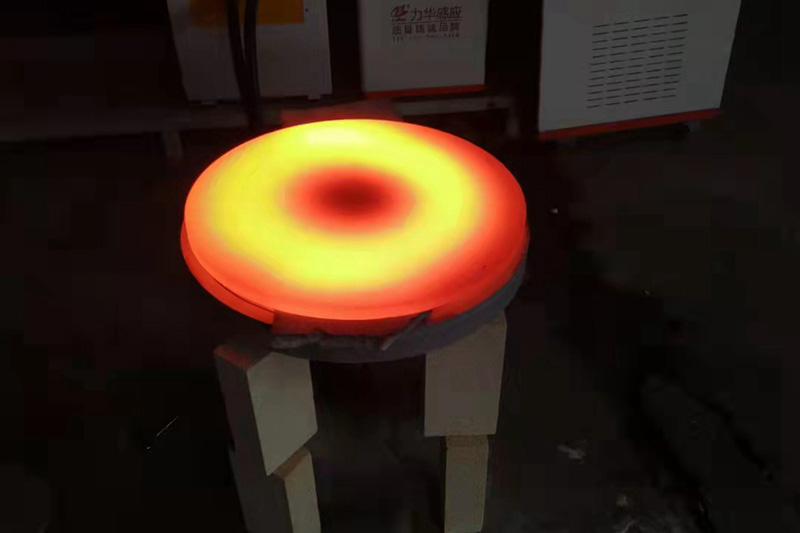
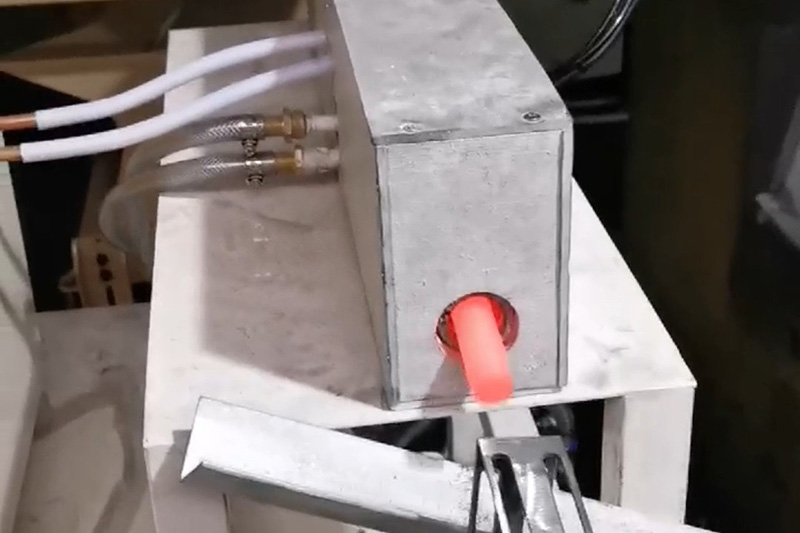
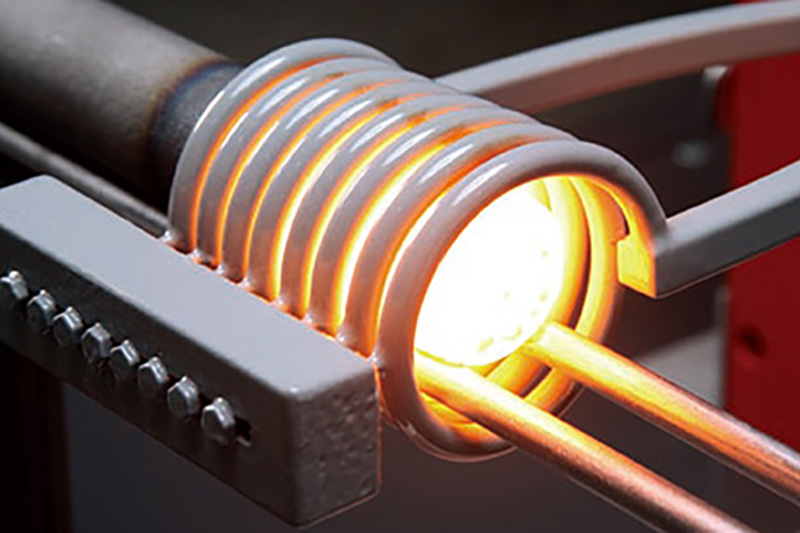
Induction forging refers to preheating metals to a certain temperature with an induction heater prior to deformation using a press or hammer. Typically steel or iron is heated to 1050 °C, copper to 700 °C to increase their malleability and aid flow in the forging die.
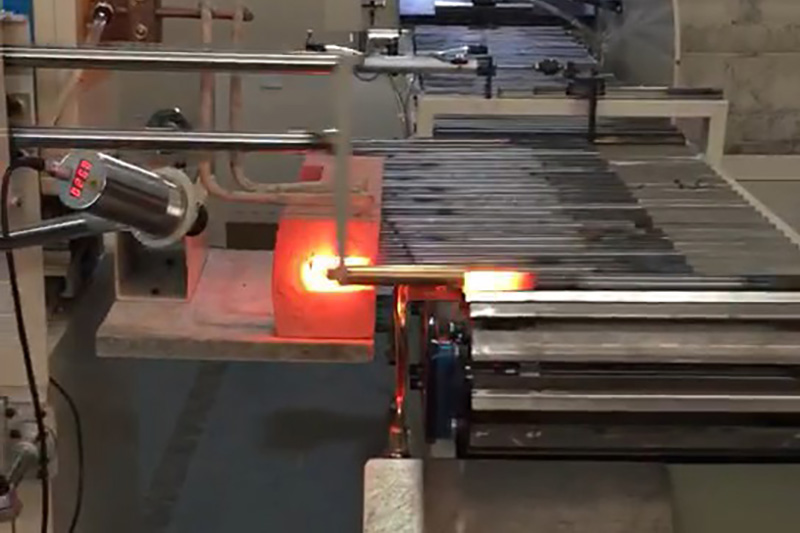
Billet heating Video
Advantages of induction forging
■ Fast heating - high throughput, less oxidative decarburization
■ Energy saving - no preheating required, only heat the workpiece excluding atmosphere around it, can accurately heat the local parts of the workpiece
■ Consistency and repeatability - the heat is extremely uniform during induction heating, which improves the accuracy of forgings, making it ideal for integration into automated production lines
■ Environmental protection - pollution-free, clean and safe working environment
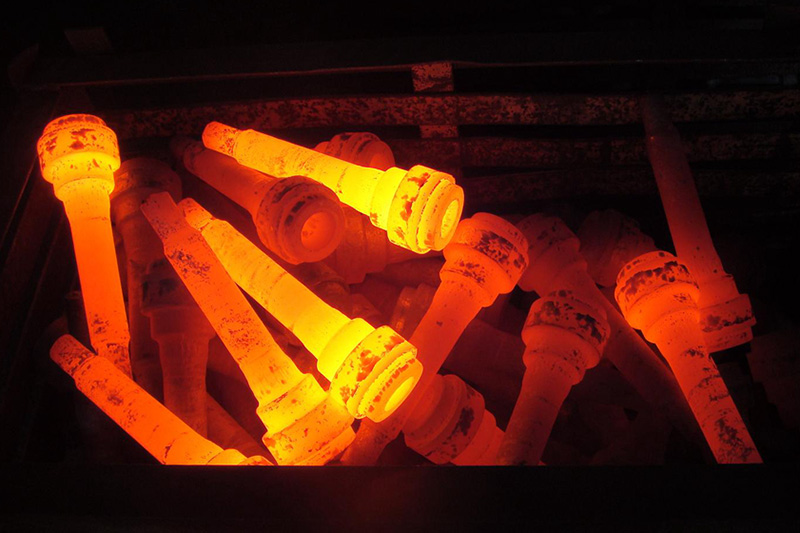
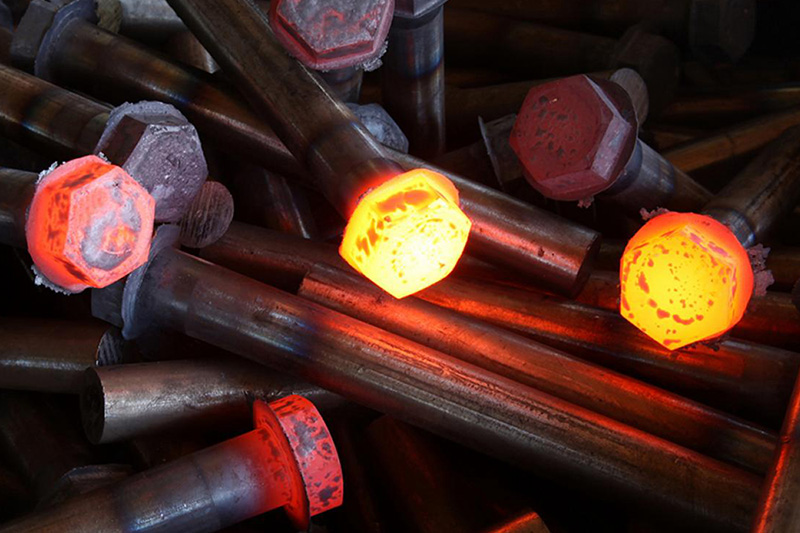
Applications of induction forging
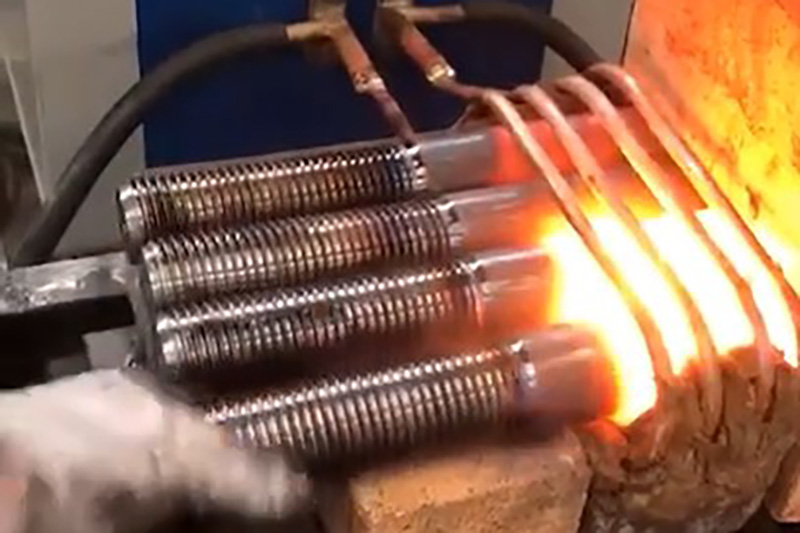
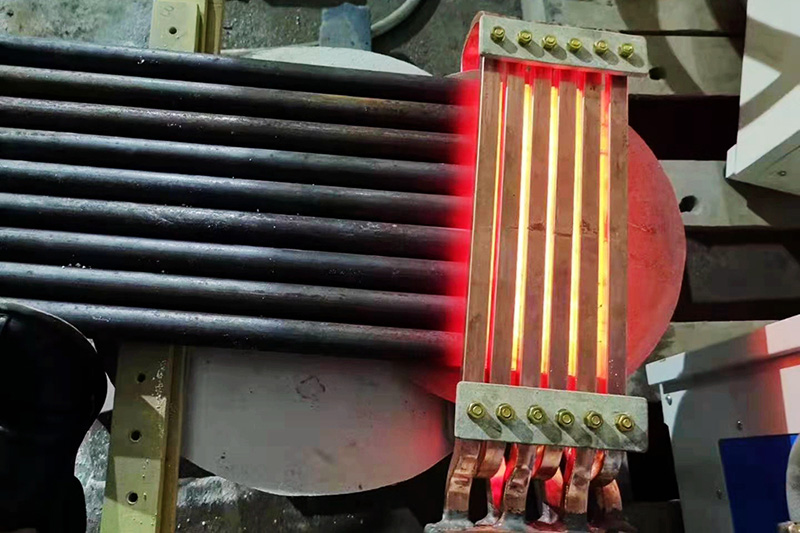
Induction forging is mainly used to heat bars, bar ends and billets with LIHUA induction heating systems. Suitable forging materials include steel, stainless steel, iron, copper, brass and aluminium. Typical processed parts are bolt heads, hammer heads, mining tools, crankshafts, camshafts, pneumatic and hydraulic fittings, engine valves etc.